What is the Average Life Expectancy in Different Countries?
Average Life expectancy is a key indicator of a nation’s overall health, quality of life, and access to healthcare. It reflects various factors such as medical advancements, nutrition, lifestyle choices, and economic conditions.
Understanding the differences in life expectancy across countries helps highlight global health trends and disparities. In this article, we will explore life expectancy by region, the factors influencing longevity, and how different countries compare in terms of average lifespan.
Deep Look into Life Expectancy
Life expectancy is the average number of years a person can expect to live based on current mortality rates. It is influenced by various factors, including genetics, lifestyle, healthcare access, economic stability, and environmental conditions.
The World Health Organization (WHO) and the United Nations (UN) regularly publish average life expectancy reports to track global trends.
Global Life Expectancy Trends
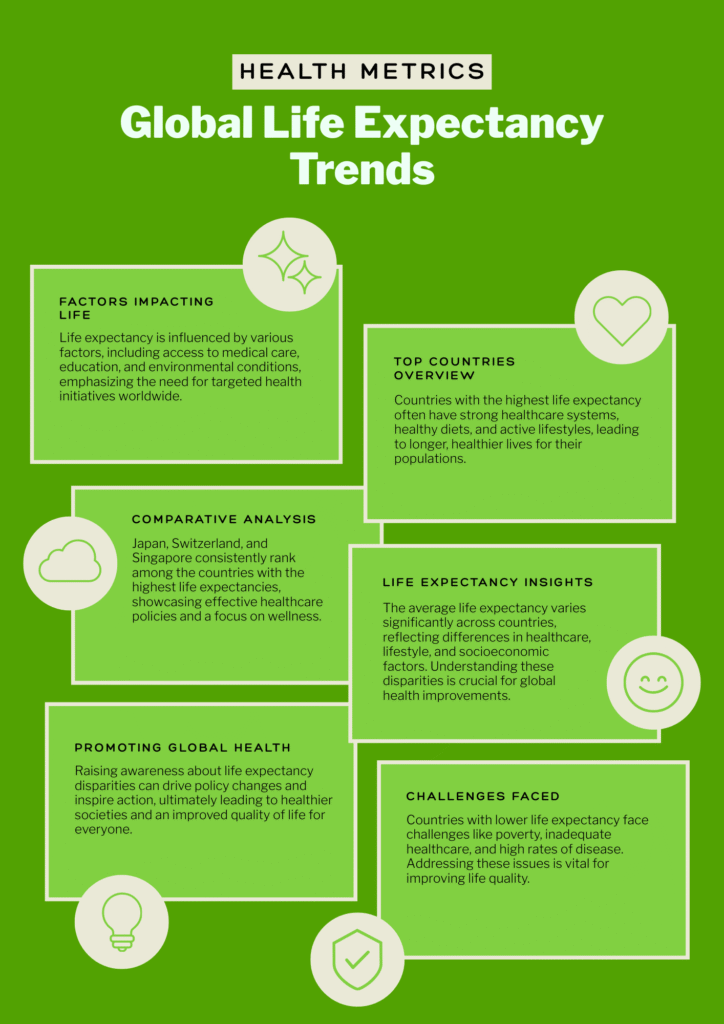
According to recent studies, the global average life expectancy is approximately 73 years. However, this number varies significantly across regions and countries due to disparities in healthcare systems, socio-economic conditions, and living standards.
Top Countries with the Highest Life Expectancy
Countries with the highest life expectancy tend to have advanced healthcare systems, higher living standards, and healthier lifestyles. Some of the top-ranking nations include:
- Japan – 84.5 years
- Switzerland – 83.8 years
- Singapore – 83.6 years
- Italy – 83.4 years
- Spain – 83.2 years
- Australia – 83.1 years
- Iceland – 82.9 years
Countries with the Lowest Life Expectancy
On the other hand, some countries face challenges such as poverty, inadequate healthcare, and political instability, leading to lower life expectancy. Countries with the lowest average lifespan include:
- Chad – 54.0 years
- Nigeria – 54.3 years
- Central African Republic – 54.6 years
- South Sudan – 55.1 years
- Somalia – 55.7 years
- Eswatini – 57.2 years
- Mali – 58.1 years

Factors Influencing Life Expectancy
Several factors contribute to differences in average life expectancy across countries. These include:
1. Healthcare System
Countries with universal healthcare coverage and advanced medical research tend to have higher life expectancy rates. Preventive care, vaccinations, and access to life-saving treatments play a crucial role.
2. Economic Development
Wealthier nations have better infrastructure, clean water, nutritious food, and higher quality medical care. In contrast, underdeveloped countries struggle with malnutrition, poor sanitation, and limited healthcare facilities.
3. Lifestyle and Diet
Diet and lifestyle habits significantly affect longevity. Countries with lower obesity rates and healthier diets, such as Japan and the Mediterranean nations, tend to have higher average life expectancy.
4. Education and Awareness
Higher levels of education lead to better awareness of healthy living, proper nutrition, and disease prevention. This often translates to improved public health and longer lifespans.
5. Political Stability and Safety
Regions with ongoing conflicts, wars, or political instability often experience lower life expectancy due to violence, displacement, and inadequate healthcare services.
6. Climate and Environment
Clean air, access to clean drinking water, and low pollution levels contribute to longer lifespans. Countries with severe environmental issues, such as high pollution and water scarcity, tend to have shorter average life expectancy.
How Life Expectancy Has Changed Over Time
Over the past century, global life expectancy has significantly improved. In the early 1900s, the global average was around 50 years. Due to medical advancements, better sanitation, and improved living conditions, this number has risen dramatically.
However, modern challenges such as rising obesity rates, mental health issues, and climate change pose new threats to life expectancy in developed nations. Meanwhile, developing countries continue to improve due to better healthcare access and economic growth.
Future Predictions for Life Expectancy
Experts predict that life expectancy will continue to increase in many parts of the world due to technological advancements in medicine, artificial intelligence in healthcare, and personalized treatments.
However, disparities between rich and poor countries may persist unless global efforts focus on reducing inequality in healthcare and economic opportunities.
Conclusion
Life expectancy is a powerful indicator of a nation’s overall well-being. While some countries boast high life expectancy due to advanced healthcare and healthy lifestyles, others struggle due to economic and political challenges.
Understanding these differences helps drive efforts to improve global health and quality of life. As medical advancements continue, the future of global longevity looks promising, but addressing inequalities remains a key challenge.
Check Out: Online Age Calculator by Date of Birth